Ranking Poker Hands Python
This is the last phase of building our super simple video poker game in Python 3, but we'll come back to this example for adding things like more modes, card.
Released:
A pure python poker hand evaluator for 5, 6, 7 cards
This code is intended to choose the best poker hand of five out of a set of cards. The cards are represented by a list of strings, where each string contains the rank and suit (e.g., 'AC' represent. I am trying to create a poker program with python where I get a hand like the one below. What I want to do do is sort the hand and then return true if it True. I need to know if it is a straight as well if it is a royal flush. This articles covers detailed description of uva 10315 the poker hands problem explanation and solution tricks with its source code in python. Keywords: poker hands, poker hands uva, poker hands problem, poker hands online judge, poker hands problem solution, uva 10315, uva 10315 solution python, poker hands source code, poker hands programming challenge.
Project description
In pure python
27 January 2011, Alvin Liang
Introduction
This is a pure python library to calculate the rank of the best pokerhand out of 5, 6, or 7 cards. It does not run the board for you, orcalculate winning percentage, EV, or anything like that. But if you giveit two hands and the same board, you will be able to tell which handwins.
It is nowhere near as fast as pypoker-eval, but it works if you can’tuse C for some reason (the early stages of the first MIT pokerbotcompetition come to mind). The core algorithm is slower, and youobviously don’t have the speed of C.
Quick Start
Rank is 2-14 representing 2-A, while suit is 1-4 representingspades, hearts, diamonds, clubs.
The Card constructor accepts two arguments, rank, and suit.
Algorithm
The algorithm for 5 cards is just a port of the algorithm that used tobe at the following URL. (I purposely broke the link because it now hostsa malware site.)httx://wwx.suffecool.net/poker/evaluator.html
I came up with the 6 and 7 card evaluators myself, using a very similarcard representation and applying some of the same ideas with primenumbers. The idea was to strike a balance between lookup table size andspeed.
Also, I haven’t included the code I used to generate the lookup tables,but you should be able to do that with a simpler, slower algorithm.Maybe I’ll add that later as well.
There is also a two-card ranking/percentile algorithm that is unrelatedto the rest and may get cleaned up later. We used it at one point forsome pre-flop evaluation. Credit to Zach Wissner-Gross for developingthis.
Documentation is sparse at the moment, sorry about that, and obviously Idid not really bother to package it or clean it up. I may or may notwork on this in the future. Basically, I made it, so why not release it?
Contributors
- Me! Go me!
- Zach Wissner-Gross (2-card algorithm)
- arslr (Fixes for other Python versions)
- Jim Kelly (Help with packaging, additional documentation)
- hwmrocker (Improvements to Card constructor, Python 3 compatibility)
- radekj (Tests, Python 3 compatibility)
Release historyRelease notifications RSS feed
0.2.0
Ranking Poker Hands Python Cheat
0.1.2
0.1.1
0.1.0
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
| Filename, size | File type | Python version | Upload date | Hashes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filename, size pokereval-0.2.0-py3-none-any.whl (573.8 kB) | File type Wheel | Python version py3 | Upload date | Hashes |
| Filename, size pokereval-0.2.0.tar.gz (568.8 kB) | File type Source | Python version None | Upload date | Hashes |
Hashes for pokereval-0.2.0-py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest |
|---|---|
| SHA256 | cbcdac21a2cbd329998c2ab39cd2e30ad4ec4215c1bf7e0ff2ff017c076472f4 |
| MD5 | cbe68a5fb778129955a054a1b62a677c |
| BLAKE2-256 | 305ab20017b8963dcc1e8a38cd74a832266ed6ea0f215d3903218358dfcc0327 |
Hashes for pokereval-0.2.0.tar.gz
| Algorithm | Hash digest |
|---|---|
| SHA256 | b85ab5cc10f9392da474b5538803ea1a89ff41a02c231f498497b3bba95f2e3a |
| MD5 | 5320a1d685ab226a3a1af118ed054d64 |
| BLAKE2-256 | ed4f987a9edbad5b35eb7a6eede7834e39c4605e2f29bcae0e212545fbcb8a90 |
Last updated: January 1, 2018
I recently took a Hackerrank challenge for a job application that involved poker. I'm not a poker player, so I had a brief moment of panic as I read over the problem the description. In this article I want to do some reflection on how I approached the problem.
The hackerrank question asked me to write a program that would determine the best poker hand possible in five-card draw poker. We are given 10 cards, the first 5 are the current hand, and the second 5 are the next five cards in the deck. We assume that we can see the next five cards (they are not hidden). We want to exchange any n number of cards (where n <= 5) in our hand for the next n cards in the deck. For example, we can take out any combination of 2 cards from the hand we are given, but we must replace these two cards with the next two cards from the deck (we can't pick any two cards from the deck).
Suit and value make up the value of playing cards. For example, you can have a 3 of clubs. 3 is the value, clubs is the suit. We can represent this as 3C.
Suits
Clubs CSpades SHeart HDiamonds D
Value (Rank)
2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, Jack, Queen, King, Ace
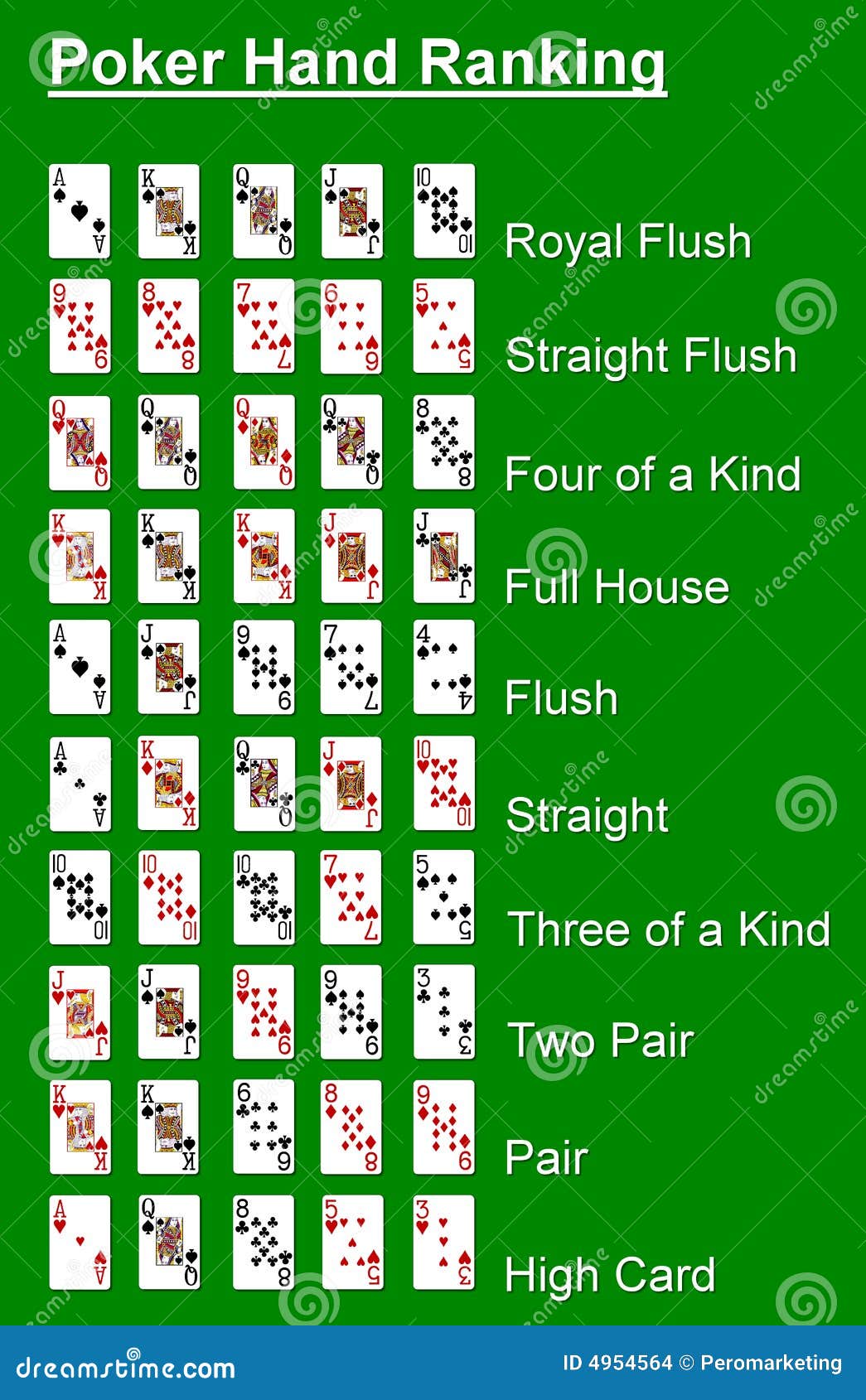
Hands
Here are the hands of poker
Royal flush (the problem didn't ask me to consider Royal Flush)
A, K, Q, J, 10, all the same suit.
Straight flush
Five cards in a sequence, all in the same suit. Ace can either come before 2 or come after King.
Four of a kind
All four cards of the same rank.
Full house
Three of a kind with a pair.
Flush
Any five cards of the same suit, but not in a sequence.
Straight
Five cards in a sequence, but not of the same suit.
Three of a kind
Three cards of the same rank.
Two pair
Two different pairs.
Pair
Two cards of the same rank.
High Card
When you haven't made any of the hands above, the highest card plays.In the example below, the jack plays as the highest card.
Evaluating a hand of cards
A hand is five cards. The first thing I did was write out functions to evaluate if a group of 5 cards satisfies the conditions of one of the ten hands.
Here's a sample hand:
To write functions, I reached for using 2 important python features: set and defaultdict.
Here's an example of a simple function to detect a flush, a hand with cards of all the same suit:
Checking a flush
This function creates a list of the suits in our hand, and then counts the unique elements in that list by making it a set. If the length of the set is 1, then all the cards in the hand must be of the same suit.
But wait, what if we have a straight flush? Also, a hand that satisfies a flush could also be described as a two pair hand. The problem asked me to find the highest possible hand for a given set of cards, so I tried to keep things simple by writing a check_hand() function that checks each hand starting from straight flush down to high card. As soon as a condition for a hand was satisfied, I returned a number that corresponded to the strength of the hand (1 for high card up to 10 for straight flush). The problem didn't include Royal flush, so I will not include that here.
Here's the check_hand function:
This function starts checking the most valuable hands. After it checks the second to lowest hand (pair), it returns a value of 1. This value of 1 corresponds to the 'highest card' hand. Since I'm not comparing the relative value of hands, it doesn't matter what the highest card is, so the number just represents the type of hand that is the strongest.
Other hands
Here are the all of the functions I used to detect hands:
defaultdict is a great built-in that is good to use when you don't know what elements will be in your dictionary, but you know what the initial values of any key that could be added should be. We don't need it here, but the alternative would be to write a very long dictionary where keys are the possible card values and the values of each key is 0.
Ranking Poker Hands Python Tutorial
It would certainly be cleaner and more efficient to write out the above functions into one large function, but I wanted to keep things simple as I was under time constraints.
The next step in the problem is to determine the best possible hand we can get given the hand we are dealt and the 5 cards on top of the deck. I decided to first solve this problem with brute force. Here was my logic for this part: use itertools to get all combinations of groups of 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 cards from my hand and add the first 5 - n cards from the deck so we get a five card deck. For each combination of cards we can run check_hand() and keep track of the highest rank hand, and then return that hand as the best hand. Here's the code I wrote for this part of the problem:
Lastly, I need to check each hand and print out the best hand possible. Here's the loop I wrote to do this:
This will accept one round of cards per line:
and it will output the following:
This was an interesting problem to deal with as the solution contained several parts that worked together. While solving the problem I aimed worked through to the end leaving some parts to come back to that I felt confident in solving. Instead of writing each function to check differnt hands at the beginning, I filled most of these functions with pass and moved on to write the next part that involves checking each different combination of cards. Recently having worked through python's itertools exercises on Hackerrank, the combinations functions was fresh in my mind.
While I was able to arrive at a solution that satisfied the test cases, I did not have time to think about the efficiency or Big O analysis of the problem.
Ranking Poker Hands Python Games
There is obviously some refactoring that I could do to make things cleaner. With more time I would take an object oriented approach by making classes for cards and hands, and adding class methods to evaluate the hands.
For each round, we have to run check_hand() on each hand combination. Let's think about how many hands we have to evaluate:
We have to consider combinations of cards formed by taking out groups of 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 cards and adding the next number of cards in the deck that bring the total card count to 5, which means we have to do 5C0 + 5C1 + 5C2 + 5C3 + 5C4 + 5C5 calls to check_hand(). So the sum of total calls is 1 + 5 + 10 + 10 + 5 + 1 = 32.
For each of these 32 calls that happen when we run play(), check_hands() runs through each of the check_ functions starting with the highest value hand. As soon as it finds a 'match', check_hands() returns a number value (hand_value) corresponding to straight flush, four of a kind, etc. This value is then compared with the highest value that has been previously found (best_hand) and replaces that value if the current hand's hand rank has a higher value.
I'm not sure if there is faster way to find the best hand than the brute force method I implemented.